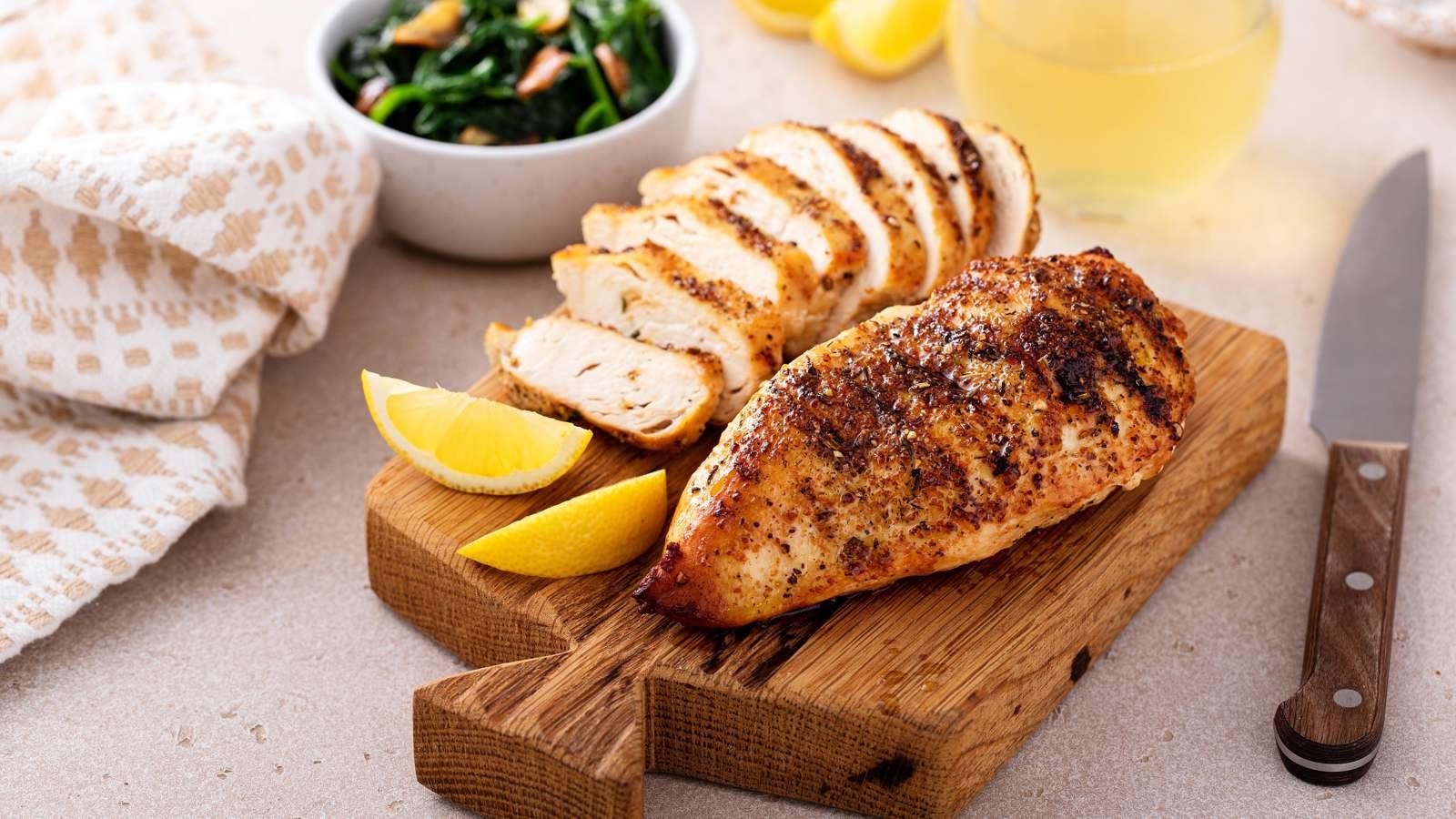
Chicken has long been considered a healthier alternative to red and processed meats, with the belief that it is more beneficial and contains lower levels of saturated fats. However, a recent study may challenge this common view, as it showed a potential link between excessive poultry consumption and an increased risk of death, particularly from digestive diseases.
Study Details:
The study was conducted by a research team from the National Institute of Digestive Diseases in Italy, which analyzed the health data of over 4,800 participants over a span of 19 years. The team tracked the participants' dietary habits, including the amount of meat and poultry consumed weekly, along with other health factors such as height, weight, and blood pressure.
Study Results:
The study revealed that people who consumed more than 300 grams of poultry per week, approximately four servings of meat, were 27% more likely to die from any cause compared to those who consumed less than 100 grams weekly. The study also showed that high poultry consumption could be linked to an increased risk of digestive system cancers, including cancers of the intestines and stomach.
The Impact of Meat Consumption on Health:
These results emphasize the importance of considering the diet as a whole and not relying on a single type of food. While white meats like poultry are considered a better option compared to red or processed meats, excessive consumption of any type of meat can have negative long-term health effects. Eating large amounts of animal proteins is a risk factor for heart disease, cancer, and some digestive system disorders.
Influencing Factors:
The study points out that several factors may contribute to the negative effects of excessive poultry consumption. For example, the preparation of poultry may lead to the addition of saturated fats or sodium, which could increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Cooking methods also play a significant role; fried or grilled poultry at high temperatures may contain carcinogenic compounds that increase the likelihood of digestive system cancer.
Prevention and Recommendations:
Although chicken can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation, the study underscores the importance of variety in food sources. Experts recommend focusing on a wide range of healthy foods such as fish, vegetables, and fruits, while reducing overall meat consumption. It is also advised to limit processed foods and saturated fats in the diet, and focus on fiber-rich foods like whole grains.
Conclusion:
This study highlights the need for balanced eating habits, as excessive poultry consumption can lead to undesirable long-term health effects. It is important to remember that a balanced and diverse diet is key to maintaining good health, and that good nutrition goes beyond simply replacing red meat with white meat; it involves making food choices that meet the body’s nutritional needs.
Reviewing this study can be a call to rethink our daily eating habits and their impact on overall health. It is essential to continue researching ways to improve dietary awareness and provide healthy food choices that align with global trends in health maintenance and disease prevention.