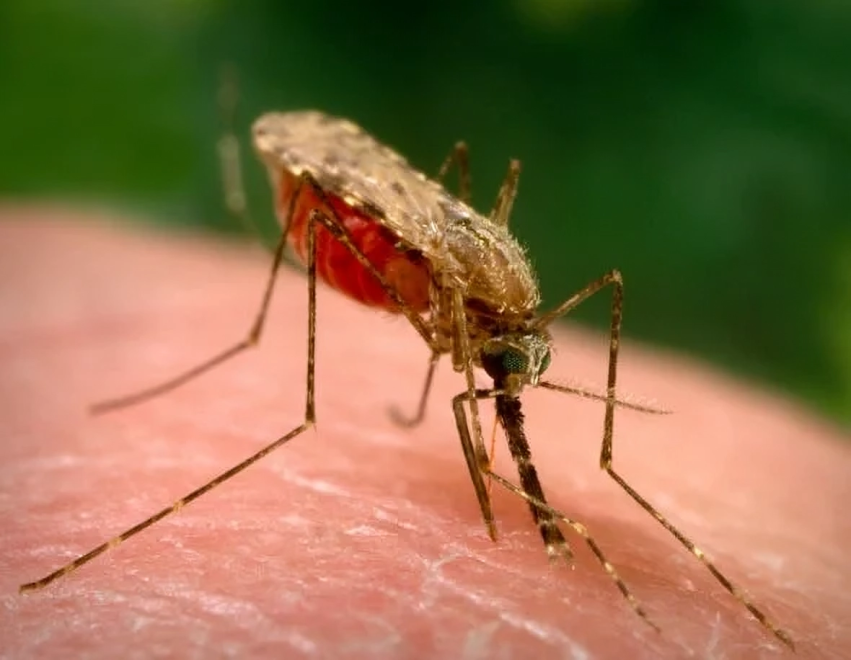
A new study has warned of the risk of malaria spreading without the need for the known mosquito bite. This insect, which carries the Plasmodium falciparum parasite, is the primary cause of malaria, one of the deadliest diseases in many parts of the world, especially in regions with hot and humid climates. The study reveals that Plasmodium falciparum, which is typically transmitted through mosquito bites, can also spread through other means such as blood transfusions and contaminated needles, complicating the health situation in certain areas.
Malaria: More Than Just a Mosquito Bite
Malaria is considered one of the most dangerous infectious diseases globally. Studies show that Plasmodium parasites are the causative agents of this disease. While malaria is typically transmitted via mosquito bites, recent research has proven that the disease can also spread through blood transfusions and contaminated needles. Plasmodium falciparum is one of the most common types, especially in African regions, while Plasmodium vivax is more prevalent outside sub-Saharan Africa.
Malaria Parasites: Types and Their Dangers
Experts indicate that there are five types of Plasmodium parasites that cause malaria. Plasmodium falciparum is the most common and causes symptoms that can rapidly worsen if left untreated. If malaria remains untreated, the disease can progress to severe stages and may lead to death within 24 hours, especially if the infection is severe.
Malaria Transmission: Not Just Mosquito Bites
It was once believed that malaria was only transmitted through mosquito bites, but new evidence shows that the disease can be spread through blood transfusions, meaning that a person could contract malaria without being bitten by a mosquito. Although malaria transmission through blood is rare, it still poses a significant risk in areas with high numbers of patients.
Malaria transmitted through blood occurs when an infected person receives blood from a donor carrying the parasite. Research has also confirmed that the infection can spread through sharing contaminated needles, which is a concern in regions with inadequate healthcare facilities or high rates of blood transfusion activities.
Initial Symptoms of Malaria: Warning Signs to Watch Out For
Malaria symptoms typically start suddenly and can resemble those of other diseases. Initial symptoms include:
Severe fatigue and exhaustion
Weakness or confusion
Multiple seizures
Difficulty breathing
Dark or bloody urine
These symptoms may indicate that the disease has progressed to a severe stage. If malaria is not treated in its early stages, it can lead to serious complications such as organ failure, severe anemia, and sepsis, which can ultimately result in death.
Impact of Malaria on the Global Health System
Malaria is not only a direct health threat but also affects the overall healthcare system. In malaria-endemic areas, hospitals are under increasing pressure due to the large number of cases. Additionally, the cost of treating the disease can place a heavy burden on individuals and the healthcare system in poor countries. Moreover, malaria contributes to an increase in other infections, making malaria control an integral part of global efforts to combat infectious diseases.
Challenges in Combating Malaria
Although malaria is a treatable disease, resistance to treatment has been increasing over time. Some studies have shown that certain malaria parasites have become resistant to the traditional drugs used to treat the disease. This makes controlling the disease more difficult, highlighting the need for new, more effective medications.
Additionally, the widespread use of insecticides to reduce mosquito populations may have negative environmental effects, reinforcing the need for new strategies to combat the disease.
Prevention of Malaria: The Importance of Preventive Measures
Preventing malaria is a top priority for public health in endemic regions. Several steps can be taken to reduce the risk of contracting this disease, including:
Using insecticide-treated bed nets during sleep.
Avoiding exposure to mosquitoes during peak times.
Taking preventive medications prescribed by doctors in endemic areas.
Taking additional precautions when administering blood transfusions, including ensuring that the blood is free of parasites.
Conclusion: Malaria is a Threat Requiring Collective Awareness
The unexpected transmission of malaria through blood and contaminated needles emphasizes the need for vigilance in all aspects of prevention and treatment. This study highlights the continued importance of scientific research and the development of effective strategies to combat malaria worldwide. Everyone, from individuals to healthcare institutions, must work together to reduce the spread of this disease and its social and health impact.