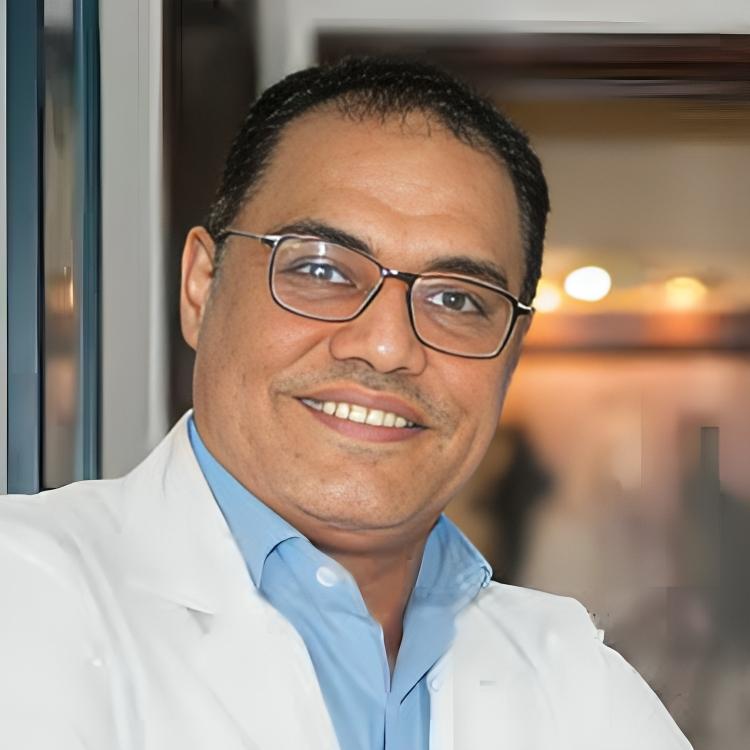
Dr. Hesham Ibrahim Mohamed Mansour
Consultant Urologist

- Name: Dr. Hesham Ibrahim Mohamed Mansour
- Phone: 01124335935
- City: Giza
- Area: Dokki
Dr. Hesham Ibrahim Mohamed Mansour
Specialization:
Kidney, Urinary and Genitourinary Surgery
Qualifications:
PhD in Kidney and Urinary Tract Surgery
Lecturer at Kasr Al Ainy Faculty of Medicine - Cairo University
Experience:
Consultant of Oncology and Endoscopy of Urinary Tract and Pediatric Urology
Memberships:
American Urological Association
European Urological Association
Egyptian Urological Association
Services Provided:
1. Urinary Tract Treatment:
Children Patients:
Treatment of Genital Deformities
Treatment of Bedwetting
Adult Patients:
Treatment of Urinary Tract Obstruction Urine
Treatment of urinary incontinence
2. Tumor surgery:
Removal of kidney and bladder tumors
Treatment of prostate cancer
3. Lithotripsy:
Removal of kidney and bladder stones using:
Laser
Endoscopy
4. Kidney surgeries:
Nephrectomy
Transurethral or open prostatectomy
Urinary tract surgery
5. Treatment of sexual dysfunction:
Various therapeutic procedures including urodynamics
6. Hemodialysis:
Providing hemodialysis services to patients in need
To communicate:
Clinic Information:
Address:
107 Tahrir St., Dokki Square, 4th Floor, Cairo
Clinic Number:
01124335935
Working Hours:
Daily from Saturday to Friday, from 4 to 7 pm
For more information or to book an appointment, you can contact the clinic on the number mentioned above. You can also visit the clinic during the specified working hours to discuss any inquiries or to obtain medical advice.
Suggested Results
Speciality: Urologists
Price: Not Available
Phone: 01113529990
WhatsApp: 01113529990
Location: Dokki, Giza
Address: next to Hassan Al-Sharbatly Mosque, First Settlement,
About the Doctor:
🌟 CV of Dr. Jody Ibrahim Mohamed 🌟
🔍 Keywords: Dr. Jody Ibrahim, urological surgery, reproductive surgery, male infertility treatment, stone fragmentation, pediatric surgery, prostate vaporization, ... Read More
FAQ
Urological surgery is a medical specialty that deals with diseases and issues affecting the urinary system (kidneys, bladder, ureters, urethra) and male reproductive organs (such as the prostate, testes, and vas deferens). This specialty includes a wide range of surgical procedures to treat various problems, such as:
- Kidney stone treatment: Using traditional or advanced surgical techniques such as stone fragmentation with lasers or shock waves.
- Treatment of chronic urinary tract infections: Such as pelvic or bladder infections.
- Correction of congenital defects: Like dilation or defects in the ureters or urethra.
- Prostate tumor removal: Whether malignant or due to benign prostate enlargement.
- Surgical treatment of varicocele: Which can affect sperm production and lead to infertility.
Male infertility can result from a variety of potential causes, some of which are related to problems with sperm production or transport, while others are associated with hormonal or environmental factors:
- Problems with sperm production:
- Low sperm count: A sperm count lower than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen is considered low.
- Poor sperm motility: Sperm may be unable to swim properly to reach and fertilize the egg.
- Abnormal sperm morphology: Abnormal shapes of sperm can affect their ability to fertilize the egg.
- Blockages in the sperm ducts: Blockages in the vas deferens or other ducts may prevent sperm from reaching the semen.
- Hormonal imbalances: Disorders in testosterone levels or pituitary gland function can affect sperm production.
- Infections: Infections such as orchitis (inflammation of the testes) or prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate) can impact male fertility.
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum can disrupt blood flow to the testes, leading to decreased sperm quality.
- Environmental and lifestyle factors: Smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, stress, exposure to chemicals or radiation, or excessive heat may all contribute to reduced fertility.
Prostatectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the prostate gland, primarily used to treat the following conditions:
- Prostate cancer: If the cancer is localized within the prostate and has not spread to surrounding tissues.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): A non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate that leads to urinary problems.
- Chronic prostatitis: When the prostate becomes inflamed, causing chronic pain and difficulty urinating.
Prostatectomy techniques include:
- Traditional open surgery: Performed through an incision in the lower abdomen.
- Laparoscopic surgery: Performed using small incisions and a camera to visualize the area being treated.
- Robotic surgery: Involving the use of robotic assistance to reduce the overall size of incisions and improve the precision of the procedure.
Yes, male infertility can be treated depending on the underlying cause. Available treatments include:
- Medications: If there is a hormonal issue, such as low testosterone, or if there are infections, medications can be used to address the cause.
- Surgery: If there is a blockage in the sperm ducts, surgery may be performed to remove the obstruction or correct abnormalities.
- Assisted reproductive technologies:
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): The woman’s egg is retrieved and combined with sperm in the laboratory, then the fertilized egg is returned to the uterus.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): A single sperm is directly injected into the egg in cases where the male has sperm production issues.
Kidney stones are solid pieces that form in the kidneys due to the accumulation of minerals. If the stones are large or cause pain, they may be treated by fragmentation. Fragmentation techniques include:
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): High-frequency sound waves are used to break the stones into small pieces so that they can be expelled through urine.
- Laser fragmentation: In cases where stones are difficult to treat with shock waves, lasers can be used to break the stones inside the kidneys or bladder.
- Surgical fragmentation: In rare cases when other methods are unsuccessful, open surgery may be performed to remove large stones.
Prostatitis occurs when the prostate gland becomes inflamed, and the causes can include:
- Bacterial infection: This may occur due to an infection that spreads through the urethra or bladder.
- Non-bacterial inflammation: Sometimes, there is no bacterial infection, but the prostate may remain inflamed due to causes that are not fully understood, such as nerve stress or issues with the nerves or muscles.
- Chronic prostatitis: In this case, the inflammation may cause persistent pelvic pain and pain during urination.
The diagnosis of male infertility begins with a comprehensive evaluation, which includes:
- Semen analysis: To examine sperm count, motility, and morphology. This analysis is considered the first step in diagnosing male infertility.
- Hormonal tests: To assess testosterone levels and pituitary hormones (such as FSH) that affect sperm production.
- Physical examination: To identify any signs of structural or health problems, such as varicocele or prostatitis.
- Ultrasound examination: To evaluate the testes and surrounding areas to detect issues like varicocele or blockages.
- Genetic tests: In some cases, genetic testing may be conducted to determine if there are hereditary issues affecting fertility.
Surgical treatments for male infertility may include:
- Removal of blockages: If there is a blockage in the sperm ducts or vas deferens, surgery can be performed to remove the obstruction or restore normal connectivity.
- Reconstruction of reproductive vessels: In cases of damage to blood vessels or other structural issues, the vessels may be repaired.
- Sperm extraction from the testes: If sperm is absent from the semen, it can be directly extracted from the testes using techniques such as testicular biopsy or sperm retrieval with a fine needle.